Java并發(fā)編程之淺談ReentrantLock
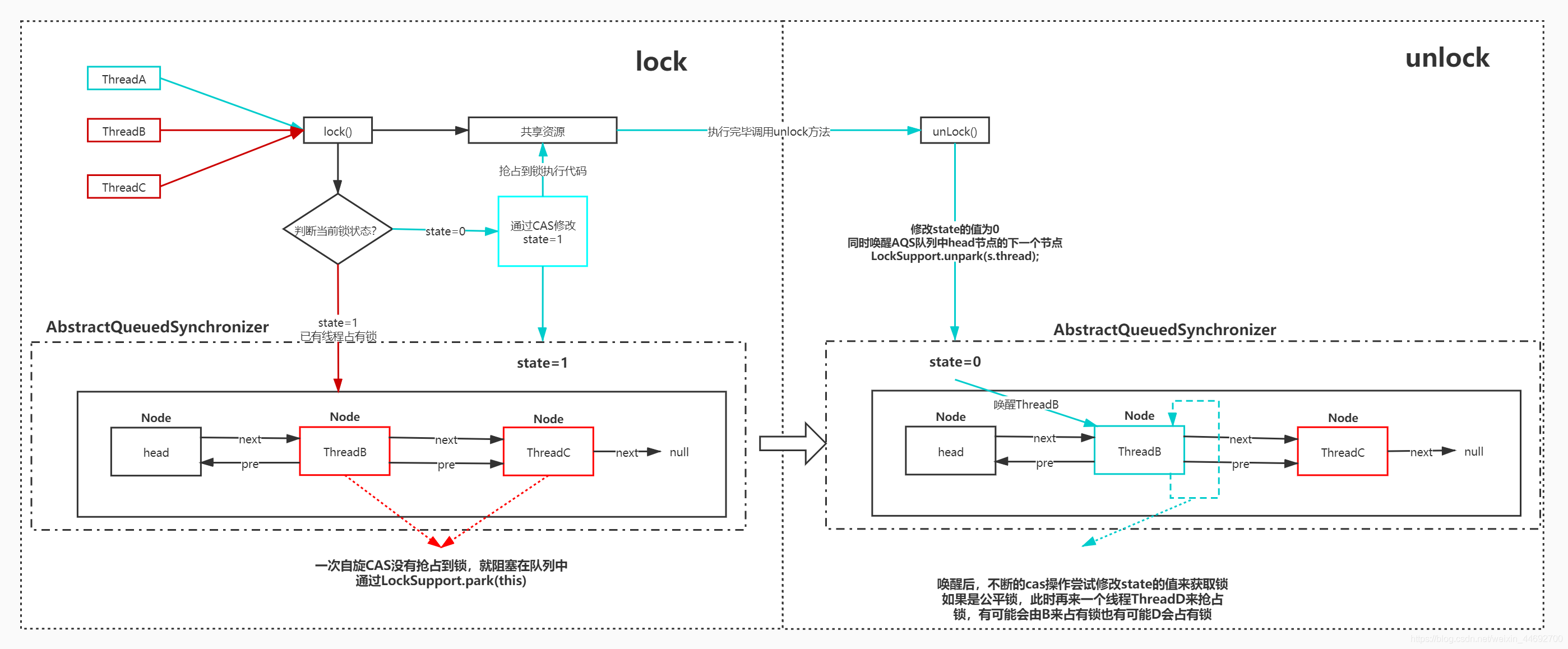
這里對公平鎖和非公平鎖做了不同實現(xiàn),由構造方法參數(shù)決定是否公平。
public ReentrantLock(boolean fair) { sync = fair ? new FairSync() : new NonfairSync();}2.1 非公平鎖實現(xiàn)
static final class NonfairSync extends Sync { private static final long serialVersionUID = 7316153563782823691L;final void lock() {if (compareAndSetState(0, 1)) setExclusiveOwnerThread(Thread.currentThread());else acquire(1); } protected final boolean tryAcquire(int acquires) {return nonfairTryAcquire(acquires); }}
代碼量很少。首先compareAndSetState(0, 1)通過CAS(期望值0,新值1,內(nèi)存值stateOffset)
如果修改成功,即搶占到鎖,setExclusiveOwnerThread(Thread.currentThread());將AQS中的變量exclusiveOwnerThread設置為當前搶占到鎖的線程,也就是圖中的ThreadA。 若沒有搶占成功,證明此時鎖被占用,執(zhí)行方法acquire(1);。public final void acquire(int arg) { if (!tryAcquire(arg) &&acquireQueued(addWaiter(Node.EXCLUSIVE), arg))selfInterrupt();}
這里主要看兩個方法tryAcquire(arg)和acquireQueued(addWaiter(Node.EXCLUSIVE), arg)。當滿足if條件后,會給當前線程標記一個interrupt狀態(tài)。
2.1.1 tryAcquire(arg)這個方法又有多個實現(xiàn)。這里看NonfairSync非公平鎖。
protected final boolean tryAcquire(int acquires) { return nonfairTryAcquire(acquires);}final boolean nonfairTryAcquire(int acquires) { final Thread current = Thread.currentThread(); int c = getState(); if (c == 0) { if (compareAndSetState(0, acquires)) { setExclusiveOwnerThread(current); return true; } } else if (current == getExclusiveOwnerThread()) { int nextc = c + acquires; if (nextc < 0) // overflow throw new Error('Maximum lock count exceeded'); setState(nextc); return true; } return false; }
在這個方法中,還不死心,首先會判斷下AQS中的state是否為0,為0也就是說距離上次嘗試獲取鎖到現(xiàn)在準備進入隊列(雙向鏈表)中這段時間內(nèi),鎖已經(jīng)被釋放,可以重新CAS嘗試獲取鎖。
如果當前鎖還是被持有狀態(tài),就是state!=0,就會判斷,當前線程是不是當前持有鎖的線程exclusiveOwnerThread,如果是,則state+1,從這里可以看出state表示的是重入次數(shù)。
全部不滿足,返回false。
2.1.2 acquireQueued(addWaiter(Node.EXCLUSIVE), arg)addWaiter
private Node addWaiter(Node mode) { Node node = new Node(Thread.currentThread(), mode); // Try the fast path of enq; backup to full enq on failure Node pred = tail; if (pred != null) {node.prev = pred;if (compareAndSetTail(pred, node)) { pred.next = node; return node;} } enq(node); return node;}
tryAcquire(arg)返回false,證明當前線程還是沒有獲取到鎖。那么就要進入隊列等待了,首先addWaiter方法,將當前線程封裝成一個Node,如果pred不為空,則將當前節(jié)點做鏈表的尾部插入,同時為了防止在此期間前序節(jié)點已經(jīng)不在隊列中了,也會運用CAS操作來執(zhí)行(期望值pred,新值node,內(nèi)存值tailOffset)。
如果前序節(jié)點為空,或者在CAS時發(fā)現(xiàn)前序節(jié)點已經(jīng)不存在了,則重新構建鏈表,將當前節(jié)點封裝的Node,加入到鏈表當中。
private Node enq(final Node node) { for (;;) {Node t = tail;if (t == null) { // Must initialize if (compareAndSetHead(new Node()))tail = head;} else { node.prev = t; if (compareAndSetTail(t, node)) {t.next = node;return t; }} }}
加入完成后,返回當前node節(jié)點,進入acquireQueued方法。
acquireQueued
final boolean acquireQueued(final Node node, int arg) { boolean failed = true; try {boolean interrupted = false;for (;;) {//獲取到當前node節(jié)點的上一個節(jié)點 final Node p = node.predecessor(); //如果當前的上個節(jié)點就是頭節(jié)點,會再次嘗試獲取鎖 if (p == head && tryAcquire(arg)) { //獲取成功,將當前節(jié)點置空,并成為新的頭節(jié)點setHead(node);//這個p已經(jīng)沒用了,防止內(nèi)存泄漏,直接指向null,下次GC時回收p.next = null; // help GC//不需要取消failed = false;//return false,不需要中斷當前線程return interrupted; } if (shouldParkAfterFailedAcquire(p, node) &&parkAndCheckInterrupt())interrupted = true;} } finally {if (failed) cancelAcquire(node); }}
這里是一個自旋操作,首先拿到當前線程封裝節(jié)點的上一個節(jié)點,如果滿足第一個if條件if (p == head && tryAcquire(arg)),證明上個節(jié)點為頭節(jié)點,則此時當前線程也會再次嘗試獲取鎖,獲取鎖成功,證明此時沒有別的線程在隊列中了,則將當前node清空并設置為頭節(jié)點,返回不需要中斷當前線程。
在第二個if條件中if (shouldParkAfterFailedAcquire(p, node) && parkAndCheckInterrupt())。走到這里證明當前線程不是第一個線程節(jié)點,或者沒有搶占到鎖,shouldParkAfterFailedAcquire這個方法見名知意,在搶占失敗后是否需要park阻塞,里面主要是用于清理雙向鏈表中被取消的節(jié)點線程和未被阻塞的節(jié)點線程。
private static boolean shouldParkAfterFailedAcquire(Node pred, Node node) { int ws = pred.waitStatus;//獲取前置節(jié)點的等待狀態(tài) if (ws == Node.SIGNAL)//前置節(jié)點的等待狀態(tài)為-1,表示前置節(jié)點在隊列中阻塞,那么當前節(jié)點也需要被阻塞在隊列中return true; if (ws > 0) {//前置節(jié)點等待狀態(tài)大于0,此前置節(jié)點已經(jīng)被取消,循環(huán)遍歷清除所有已被取消的節(jié)點。do { node.prev = pred = pred.prev;} while (pred.waitStatus > 0);pred.next = node; } else {//前置節(jié)點等待狀態(tài)小于等于0,且不等于-1,也就是沒有被阻塞也沒有被取消//則將前置節(jié)點設置為阻塞狀態(tài)。compareAndSetWaitStatus(pred, ws, Node.SIGNAL); } return false;} 前置節(jié)點的等待狀態(tài)為-1,表示前置節(jié)點在隊列中阻塞,那么當前節(jié)點也需要被阻塞在隊列中 前置節(jié)點等待狀態(tài)大于0,此前置節(jié)點已經(jīng)被取消,循環(huán)遍歷清除所有已被取消的節(jié)點。 前置節(jié)點等待狀態(tài)小于等于0,且不等于-1,也就是沒有被阻塞也沒有被取消。則將前置節(jié)點設置為阻塞狀態(tài)。
到這里,基于非公平鎖的實現(xiàn)結束。
2.2 公平鎖實現(xiàn)公平鎖和樂觀鎖的區(qū)別就在于,非公平鎖acquire(1)前會先嘗試獲取鎖,公平鎖直接acquire(1)。
static final class FairSync extends Sync {private static final long serialVersionUID = -3000897897090466540L;final void lock() { acquire(1);}}2.2.1 tryAcquire(arg)
在tryAcquire中也和非公平鎖有一定的區(qū)別。在當前鎖沒有被占有時。非公平鎖不用考慮目前AQS隊列中的排隊情況,直接通過CAS嘗試獲取鎖。公平鎖會看目前隊列的狀態(tài),再來決定是嘗試占有鎖還是在隊列中等待。
protected final boolean tryAcquire(int acquires) { final Thread current = Thread.currentThread(); int c = getState(); if (c == 0) { if (!hasQueuedPredecessors() && compareAndSetState(0, acquires)) { setExclusiveOwnerThread(current); return true; } } else if (current == getExclusiveOwnerThread()) { int nextc = c + acquires; if (nextc < 0) throw new Error('Maximum lock count exceeded'); setState(nextc); return true; } return false;}
到此這篇關于Java并發(fā)編程之淺談ReentrantLock的文章就介紹到這了,更多相關Java ReentrantLock內(nèi)容請搜索好吧啦網(wǎng)以前的文章或繼續(xù)瀏覽下面的相關文章希望大家以后多多支持好吧啦網(wǎng)!
相關文章:
1. ASP.NET MVC遍歷驗證ModelState的錯誤信息2. Vue+Spring Boot簡單用戶登錄(附Demo)3. 深入理解Android熱修復技術原理之資源熱修復技術4. PHP用代碼實現(xiàn)文件下載5. 用JS實現(xiàn)飛機大戰(zhàn)小游戲6. ASP.NET MVC使用typeahead.js實現(xiàn)輸入智能提示功能7. IntelliJ IDEA安裝插件的方法步驟8. Intellij IDEA連接Navicat數(shù)據(jù)庫的方法9. html小技巧之td,div標簽里內(nèi)容不換行10. python和JavaScript哪個容易上手
 網(wǎng)公網(wǎng)安備
網(wǎng)公網(wǎng)安備