Django認證系統user對象實現過程解析
User對象
User對象是認證系統的核心。它們通常表示與你的站點進行交互的用戶,并用于啟用限制訪問、注冊用戶信息和關聯內容給創建者等。在Django的認證框架中只存在一種類型的用戶,因此諸如’superusers’或管理員’staff’用戶只是具有特殊屬性集的user對象,而不是不同類型的user對象。
創建users
創建users最直接的方法是使用create_user()輔助函數:
>>> from django.contrib.auth.models import User>>> user = User.objects.create_user(’john’, ’lennon@thebeatles.com’, ’johnpassword’)
from django.contrib.auth.models import Userdef create_user(request): #auth_user # user = User.objects.create_user(’john’, ’lennon@thebeatles.com’, ’johnpassword’) #superuser python manage.py createsuperuser --username=joe --email=joe@example.com u = User.objects.get(username=’john’) u.set_password(’new password’) u.save() return HttpResponse('success-----%s'%u)
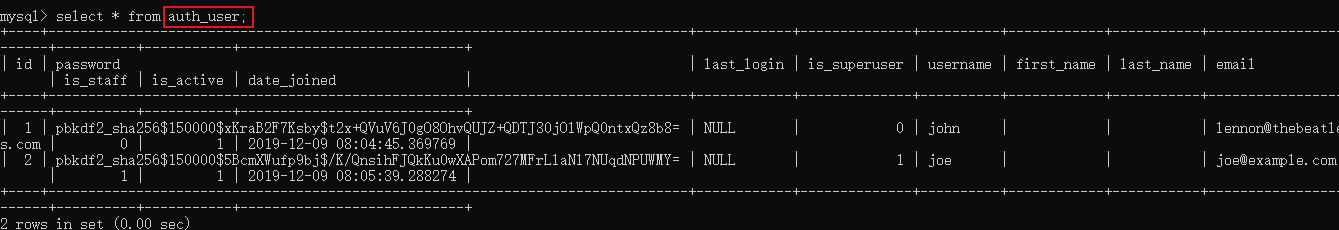
創建成功后見數據庫auth_user表
創建superusers
使用createsuperuser命令創建superusers:
$ python manage.py createsuperuser --username=joe --email=joe@example.com
或者
$ python manage.py createsuperuser
接下來依次輸入用戶密碼即可成功后見auth_user表
修改密碼
>>> from django.contrib.auth.models import User>>> u = User.objects.get(username=’john’)>>> u.set_password(’new password’)>>> u.save()
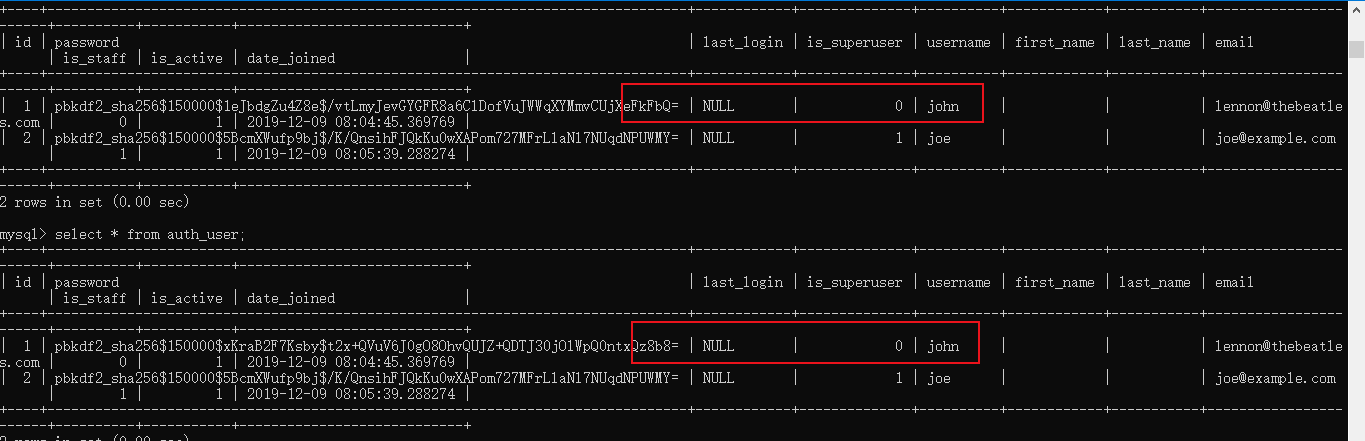
成功后見auth_user表,密碼已經改變
認證Users
authenticate(**credentials)[source]
認證一個給定用戶名和密碼,請使用authenticate()。它以關鍵字參數形式接收憑證,對于默認的配置它是username和password,如果密碼對于給定的用戶名有效它將返回一個User對象。如果密碼無效,authenticate()返回None。例子:
from django.contrib.auth import authenticateuser = authenticate(username=’john’, password=’secret’)if user is not None: # the password verified for the user if user.is_active: print() else: print()else: # the authentication system was unable to verify the username and password print()
def auth(request): user = authenticate(username=’john’, password=’new password’)#john # user = authenticate(username=’john’, password=’johnpassword’)#None print(user) if user is not None: # the password verified for the user if user.is_active: print('驗證成功,已激活') else: print('驗證成功,未激活') else: # the authentication system was unable to verify the username and password print('沒有此用戶') return HttpResponse(user)
john
驗證成功,已激活
以上就是本文的全部內容,希望對大家的學習有所幫助,也希望大家多多支持好吧啦網。
相關文章:

 網公網安備
網公網安備